Liquid Metal Cooling: Keeping Tech Chill in a Heating World
In the ceaseless race for more powerful computing, one peculiar substance is making waves: liquid metal. Once the stuff of science fiction, this fascinating material is now being harnessed to cool down our devices, from gaming PCs to data centers. How did we get there, and what does the future hold for this high-tech coolant?
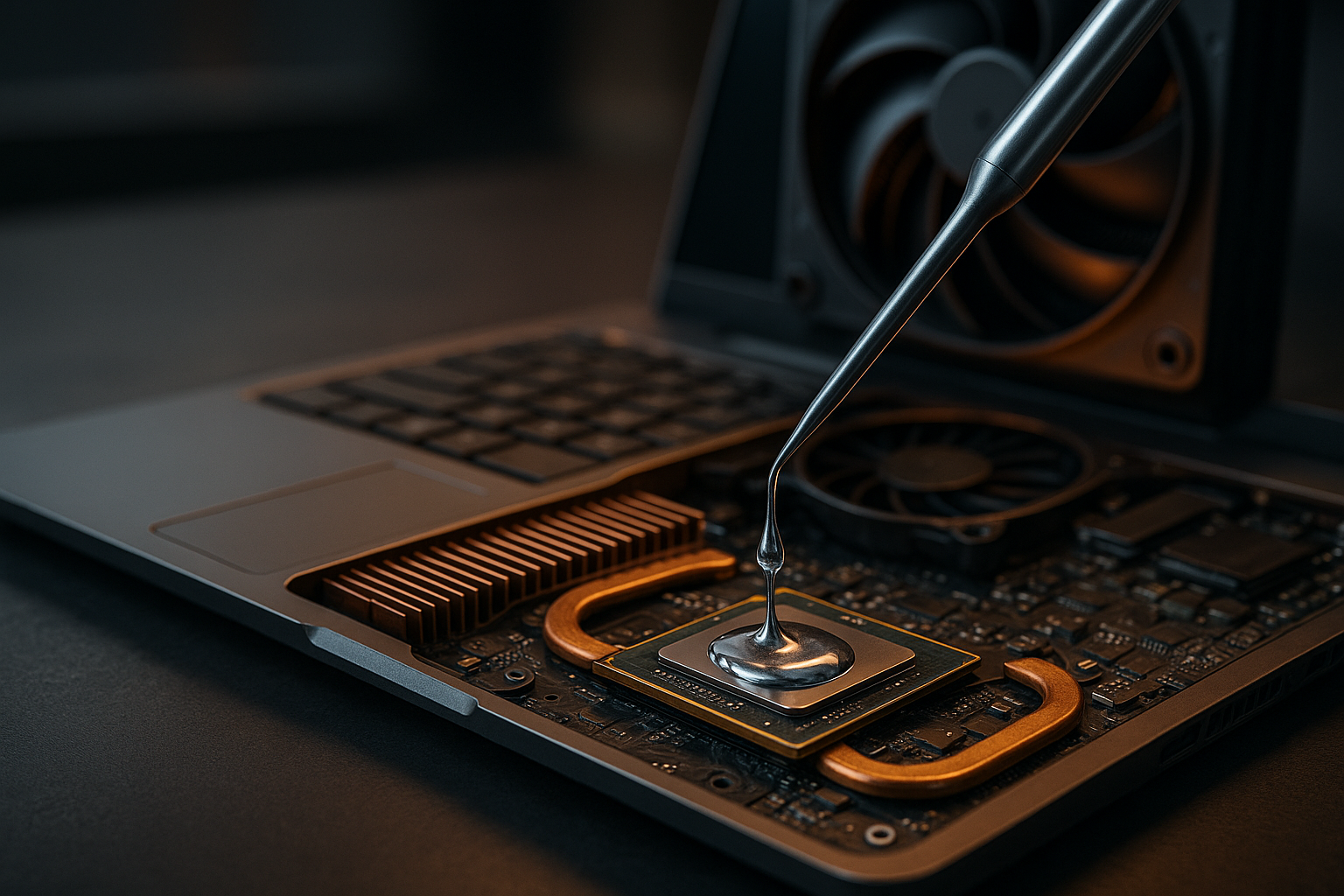

A Brief History of Cooling Tech
In the early days of computing, machines were so simple and slow that they didn’t generate much heat. As technology advanced, processors became faster and more complex, producing more heat. Engineers needed a way to keep these machines cool to prevent overheating and damage.
First came fans, then heat sinks, and finally, liquid cooling systems. But these solutions weren’t perfect. Fans were noisy and inefficient. Heat sinks were bulky and could only dissipate so much heat. Liquid cooling systems were better, but they required a lot of maintenance and could leak, damaging the machine.
Enter liquid metal cooling.
What is Liquid Metal Cooling?
Liquid metal cooling is a thermal management solution that uses liquid metal as a coolant. Unlike traditional coolants, liquid metals have high thermal conductivity, meaning they can absorb and transfer heat more efficiently.
The concept isn’t new. It’s been used in nuclear reactors for decades. But only recently have scientists and engineers started exploring its potential for cooling electronic devices. The most commonly used liquid metal for this purpose is a gallium-based alloy, which remains liquid at room temperature and doesn’t corrode electronic components.
The Current State of Liquid Metal Cooling
In recent years, several tech companies have started to take liquid metal cooling seriously. ASUS, a leading manufacturer of gaming PCs and laptops, has already incorporated it into some of its high-end laptops. The results have been impressive, with significant reductions in operating temperatures and performance improvements.
Data centers, which consume vast amounts of energy and generate a lot of heat, are another area where liquid metal cooling could make a big difference.
Impact and Potential of Liquid Metal Cooling
The implications of liquid metal cooling are vast. For one, it could enable even more powerful computing without the risk of overheating. It could also make devices more energy-efficient, as less energy would be wasted as heat.
The price of implementing liquid metal cooling is still relatively high, but as the technology matures and becomes more widespread, costs are likely to come down.
The Future of Liquid Metal Cooling
As we push the limits of computing power, the need for efficient cooling solutions will only increase. Liquid metal cooling, with its high thermal conductivity and compatibility with electronic components, is well placed to meet this demand.
In the future, we may see it used in everything from supercomputers to smartphones, helping to keep our devices cool as we continue to demand more from them.
In conclusion, as we push the boundaries of technological innovation, liquid metal cooling is poised to play a critical role in keeping our devices cool and efficient. Its impact on the tech industry could be as transformative as the microchip itself – and that’s no small feat.